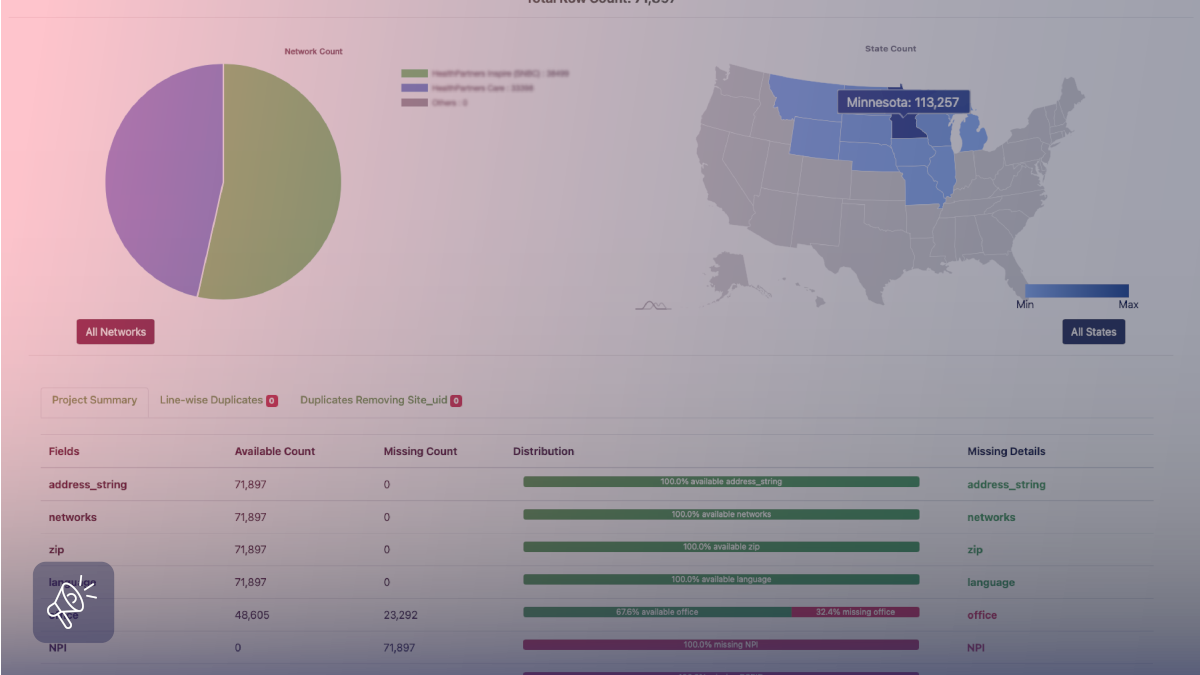
If you have ever needed “the latest competitor prices before the 10 a.m. stand-up,” you already know the real challenge is not just getting to the page, but seeing the same thing a human would see and doing it at scale without slowing your team down.
Headless browser scraping makes this possible by opening pages like a real user, running the site’s JavaScript, handling sessions, and pulling out the fields you care about, all while staying quiet in the background so you can focus on results instead of servers.
Understanding Headless Browsers in Data Extraction
A headless browser is simply a standard browser that runs without showing a window. It still loads pages, runs scripts, stores cookies, and follows redirects, which means the data it captures matches what a person would see.
Because there is no interface to draw, each run uses fewer resources and usually finishes sooner, making headless browser scraping a good fit for scheduled refreshes, event-based triggers, and on-demand jobs that require reliability.
Teams get fewer surprises when content appears only after an interaction, and dashboards stay aligned with the experience users actually have in a real browser.
Why Headless Browsers?
Headless browser scraping enables development and data teams to work faster while maintaining high quality on modern, JavaScript-heavy sites.
Efficiency: With no visible UI, your jobs spend more time on page logic and extraction rather than rendering, improving throughput as concurrency increases.
Automation: Scripts can log in, scroll, click, choose filters, and submit forms, so you collect dynamic content that simple HTTP clients often miss.
Accuracy: Because the browser executes the site’s own code, the fields you extract reflect the real page state, which builds trust in downstream reports, models, and alerts.
To maximize the benefits of this approach, select web automation tools that align with your stack and targets. The two most common choices are Puppeteer and Selenium, each with its own strengths.
Exploring Puppeteer for Headless Browser Scraping
Puppeteer is a Node.js library from Google that controls Chrome or Chromium through the DevTools Protocol. Teams that prefer JavaScript often choose Puppeteer scraping because it provides fine-grained control over navigation, waits, and network behavior without the overhead of a large framework, keeping projects simple to start and easy to grow.
Key Features of Puppeteer
Puppeteer supports full interactions such as scrolling, clicking, typing, and file uploads, which is useful when pages reveal content only after user actions. It starts in headless mode by default and containerizes cleanly, so deploying to serverless or container services feels straightforward. Since it speaks directly to DevTools, you can intercept requests, adjust headers, track performance, and select DOM elements precisely, which improves resilience when a site changes.
Practical Applications of Puppeteer Scraping
Puppeteer works well for single-page applications where listings and details load after JavaScript runs, and it can wait intelligently for selectors or network idleness so runs stay fast without being fragile. It can also generate PDFs for audits and archival needs, and it can capture basic performance signals during each run, so you notice drift in latency or error rates before they become a production issue.
If you want these outcomes without maintaining infrastructure, Grepsr Services can design and operate a managed pipeline that turns Puppeteer scraping into a dependable data feed.
Leveraging Selenium for Web Automation
Selenium began in functional testing and now powers automation across several browsers and languages. When projects require cross-browser checks, your team prefers Python or Java, or you want to reuse testing assets for extraction, Selenium scraping becomes a natural fit that aligns with enterprise standards and CI pipelines.
Selenium’s Unique Strengths
Selenium supports Chrome, Firefox, and Edge, which helps when a source behaves differently by browser or when compliance requires multi-browser validation. A large ecosystem provides examples, plugins, and Grid options for distributed execution, while mature language bindings enable teams to leverage their existing skills.
Selenium in Data Scraping
Selenium is useful when you want regression tests that also collect data, because you confirm rendering and behavior while extracting the fields you need. It handles complex flows that involve multi-step logins, conditional elements, and form submissions, and it can run the same script across different browsers for quality checks. If Selenium scraping matches your stack better, Grepsr supports that pattern as well, with outcomes you can review in Grepsr Case Studies and engagement options in Grepsr Services.
Choosing the Right Web Automation Tool
The choice between Puppeteer and Selenium depends on your workload rather than a single rule. If you target Chrome or Chromium and your team is comfortable with Node.js, Puppeteer often enables you to achieve a stable scraper more quickly with less setup. If you need cross-browser coverage, prefer Python or Java, or want testing and scraping to live in the same suite, Selenium is often the better option.
Many teams use both, utilizing Puppeteer for high-throughput Chrome jobs and Selenium for validation or sources that require a specific browser.
Why Choose Grepsr for Web Automation and Data Solutions?
Getting a script to work once is not the end of the job. Real value shows up when the pipeline is durable, observable, and compliant at scale. Grepsr monitors sources, scales headless jobs in the cloud, applies rule-based and AI-assisted validation, and delivers clean datasets to your lake, warehouse, or applications on a reliable schedule. We help you avoid brittle selectors, respect site terms and local laws, and protect sensitive fields, ensuring governance remains intact.
If your roadmap includes predictive analytics using web scraping, our enrichment and quality layers make sure models start with trusted inputs. You can explore capabilities in Grepsr Tools and see real outcomes in Grepsr Case Studies.
Conclusion
Headless browser scraping lets your automation behave like a real user while staying efficient enough for large-scale collection. With web automation tools such as Puppeteer and Selenium, you gain the control needed for modern, JavaScript-heavy sites without heavy infrastructure.
Choose the tool that fits your stack, split work into small, reliable steps, and invest early in validation and monitoring so stakeholders trust the results. When you would rather focus on insights than upkeep, Grepsr can operate the pipeline and stand behind freshness and quality with clear SLAs.
FAQs: Headless Browser Scraping
1. What is headless browser scraping?
Headless browser scraping uses a real browser without a visible window to load pages, run JavaScript, and extract data, which helps when content is rendered on the client side.
2. Why should developers use Puppeteer over other tools?
Puppeteer integrates closely with Chrome and Chromium, offers precise control through DevTools, and runs headless by default, which makes it a quick and dependable choice for many data extraction jobs.
3. How does Selenium differ from Puppeteer?
Selenium supports multiple browsers and several languages, which suits cross-browser requirements and teams that standardize on Python, Java, or C#, while Puppeteer focuses on Chrome in a Node.js workflow.
4. Are these tools suitable for scraping dynamic content?
Yes. Both can wait for specific elements, scroll, click, and manage sessions, and they work reliably when you use smart waits and retries rather than fixed sleeps.
5. Can Grepsr assist with automation projects using these tools?
Yes. Grepsr designs and operates pipelines based on Puppeteer and Selenium, adds monitoring and AI-assisted validation, and delivers structured data where you need it with service-level commitments.
6. Is coding expertise required to use these tools effectively?
Basic programming skills are required to script navigation, waits, and parsing, although a managed partner can handle the engineering, hosting, and ongoing maintenance.
7. How do headless browsers contribute to efficient resource use?
By skipping the graphical interface, headless runs usually use less CPU and memory and complete sooner, which improves throughput and keeps costs under control.